永井 信夫
(ながい・のぶお)
Nobuo Nagai
略歴
- 大阪大学大学院生物化学専攻後期博士課程修了
- 味の素㈱中央研究所研究員、浜松医科大学生理学第二講座助手、ベルギー王国・ルーヴァン大学分子血管生物学センター研究員、近畿大学医学部第二生理学講座講師を経て本学へ
- 実験動物1級技術者
動物生理学研究室
卒業研究テーマ例
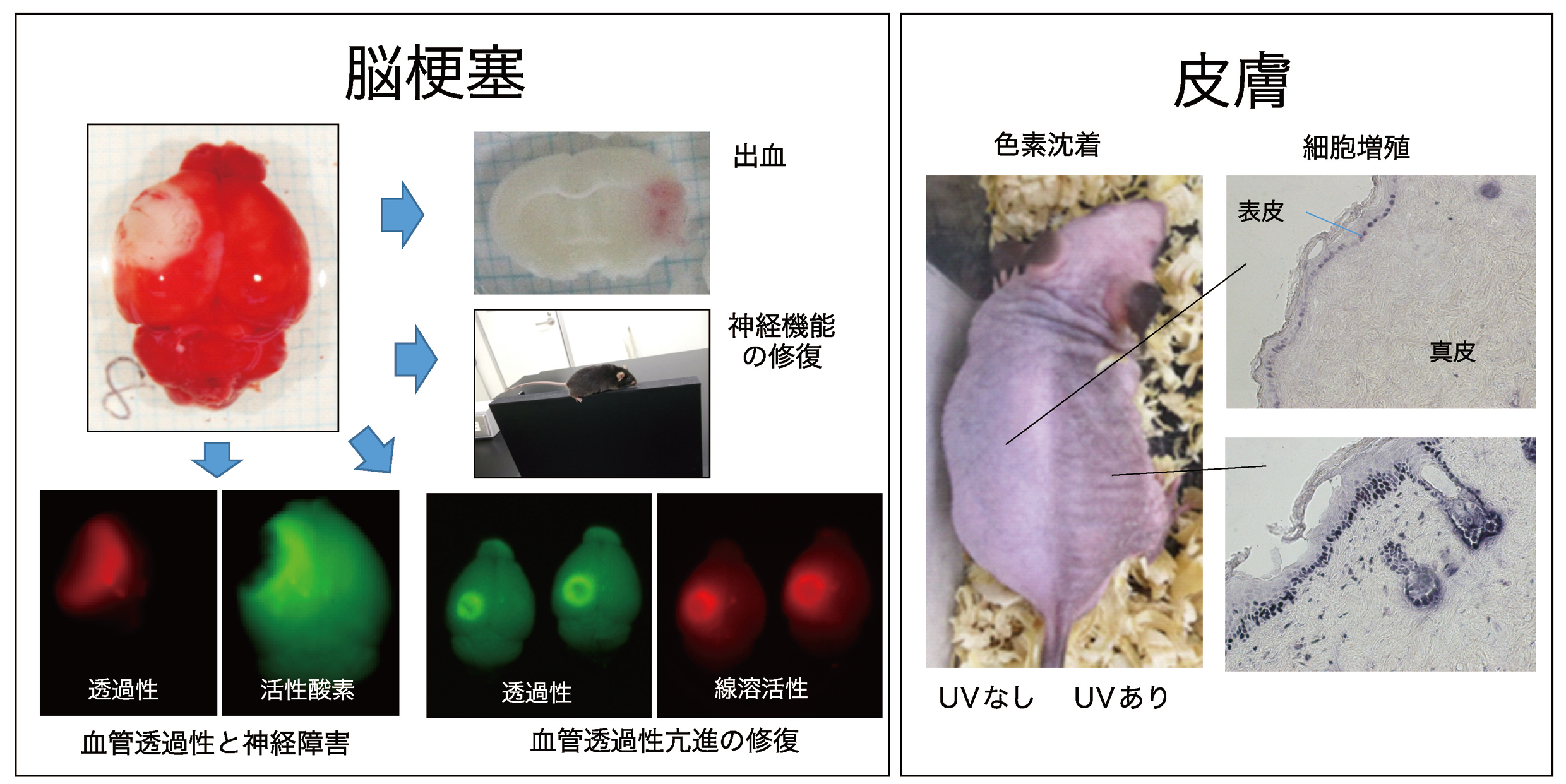
- 脳梗塞に伴う出血亢進と線溶系の関与の検討
- 新規肺塞栓モデルの確立と肺塞栓の病態形成メカニズムの解明
- 皮膚光老化における線溶系の関与の検討
新規病態モデルの作成と創薬ターゲット
線溶因子の機能の解明
- 研究の応用領域
- 医薬品・診断薬の開発、創薬分野の新技術開発
- 産官学連携で求めるパートナー
- 医薬品・診断薬開発の関連企業、大学、国・地方自治体の研究機関
In our laboratory, we study mechanisms of pathogenesis of various disease by using experimental animals and survey novel therapeutic targets. Especially, since tissue remodeling is associated with many diseases, we focus to study the roles of fibrinolytic components which is involved in tissue remodeling.
Establishment of new animal model and drug development target
Since many factors are involved in the pathogenesis of diseases, animal models are required for studying their pathogenic mechanisms. We are, therefore, developing novel animal models. By using these models, we try to clarify the mechanisms and find novel therapeutic targets.
Roles of fibrinolytic system components
The fibrinolytic system is a extracellular protease cascade with is involved not only fibrinolysis but also tissue remodeling. Since tissue remodeling is important for pathogenesis in various disease, We now studies the roles of the fibrinolytic system components. Especially, we focus on ischemic stroke, hypersensitivity and photo-aging of skin.
Kunoh T, Wang W, Kobayashi H, Matsuzaki D, Togo Y, Tokuyama M, Hosoi M, Koseki K, Wada S, Nagai N, Nakamura T, Nomura S, Hasegawa M, Sasaki R, Mizukami T. Human Dynactin-Associated Protein Transforms NIH3T3 Cells to Generate Highly Vascularized Tumors with Weak Cell-Cell Interaction. PLoS One. 2015 ; 10 : e0135836.
Suzuki Y, Nagai N, Yamakawa K, Muranaka Y, Hokamura K, Umemura K. Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator transiently enhances blood-brain barrier permeability during cerebral ischemia through vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated endothelial endocytosis in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015 ; 35 : 2021-31.
Ohmori C, Sakai Y, Matano Y, Suzuki Y, Umemura K, Nagai N. Increase in blood-brain barrier permeability does not directly induce neuronal death but may accelerate ischemic neuronal damage. Exp Anim. 2018; 67: 479-486.
Matano Y, Nojiri Y, Nomura M, Masuda A, Moriike Y, Suzuki Y, Umemura K, Nagai N. Repair of brain damage size and recovery of neurological dysfunction after ischemic stroke are different between strains in mice: evaluation using a novel ischemic stroke model. Exp Anim. 2021; 70: 344-354.
シリーズ<栄養と疾病の科学>血栓症と食 第5章 栄養と血栓溶解 pp143-169. 2020年 朝倉書店






