バイオサイエンス学科 臨床検査学プログラム
 高宮 脩(たかみや・おさむ)
高宮 脩(たかみや・おさむ)
Osamu Takamiya
専門分野/臨床検査学、血栓止血学
研究キーワード/血栓止血学、臨床検査学、血液凝固第VII因子
職位:客員教授
学位:医学博士(奈良県立医科大学)
- 大阪工業大学工学部応用化学科卒業、奈良県立医科大学小児科学専修生学位取得退学
- 信州大学医学部保健学科教授、同大学院医学系研究科教授、同大学名誉教授
研究テーマ
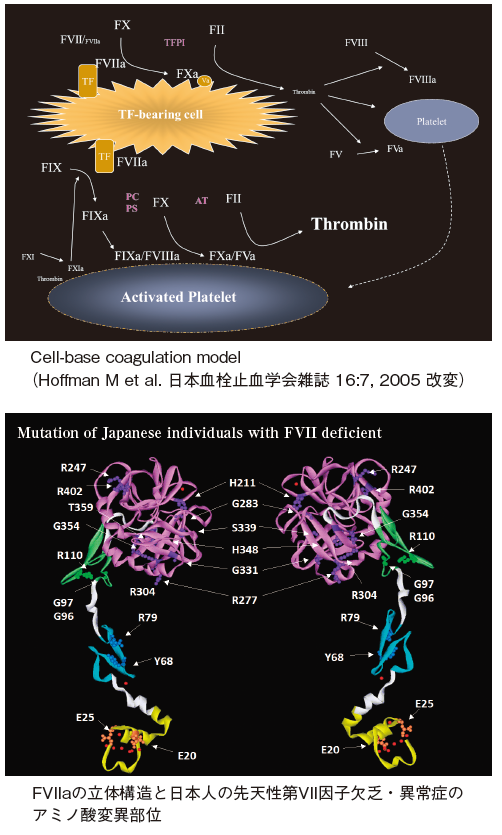
血液は血管内腔を通じて各臓器や細胞に酸素や栄養分、シグナル伝達物質を運搬するため常に流動性を保って循環しているが、血管障害によって血管外への漏出が生じた時には最小限に止める機能を有する。この生体防御反応は止血機構と称され、血管内皮細胞の種々の因子、血小板、凝固因子、線溶因子、生理的阻害因子ならびに血流や血液粘度が関わる。これらに異常が起こると出血や血栓を生じる。血栓止血検査はそれらの原因を調べ、その病態、診断や治療をサポートする。
血液凝固第VII 因子欠乏・異常症の分子病態の解析
止血の初期反応に関わる第VII 因子(FVII)の先天性欠乏・異常症の分子病態を明らかにするため、遺伝子解析に基づいた変異型FVIIを発現させて機能解析を行ってきた。本疾患は50万に1人の発生頻度と推定される稀な先天性凝固障害症である。遺伝子変異が明らかにされた国内の先天性FVII欠乏・異常症は34家系55例が報告され、22 ヶ所にアミノ酸変異が見られた。これらの変異の半数は日本人に特有ものである。本研究は患者さんの同意と医療機関および解析者機関の医倫理委員会の承認を必要とする。
血液凝固診断試薬の評価と開発
先天性FVII 欠乏症は血友病とは違って、出血症状と検査成績の相関が乏しいことが知られている。臨床検査の立場からこの原因を探るため、いくつかの視点から検討し、市販測定試薬および標準血漿、ならびにこれらの組み合わせに問題があることが解った。さらに、FVII 欠乏血漿サンプルを全国の58病院検査部の協力をえてsurveyを行ったが、FVII:Cの低値サンプルで施設間差のあることが明らかとなった。今後も血液凝固診断試薬、標準血漿、測定装置、測定法の評価、改良を続けたい。
血栓性疾患の予防のため投与されるwarfarinのモニタリングに使われるOwren-typeの試薬はウシ脳抽出物からのトロンボプラスチンが用いられてきたが、狂牛病のためウシ脳を用いることが出来なくなった。カイコを用いて遺伝子組み換え型ウシ組織因子を発現させた新規試薬を作成して、有用性のあることを報告した。これまで培ってきた臨床検査経験や知識、情報に基づき新規の凝固・線溶試薬の開発を行いたい。
| 研究の応用領域 | 産官学連携で求めるパートナー |
|---|---|
| 変異第VII 因子の分子病態、診断試薬の開発・改良 | 医療機関、診断試薬関連企業 |
Topics of research
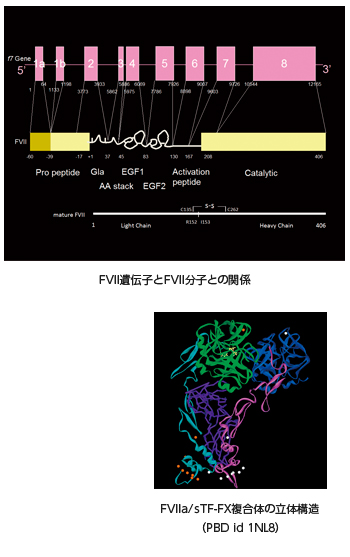 Factor VII (FVII) participates in the initial stages of blood coagulation. It is a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein that is synthesized in the liver, secreted into the blood and circulates as a single-chain zymogen composed of 406 amino acid residues with an approximate molecular weight of 50 kDa. The light chain consists of an aminoterminal γ-carboxyglutamic acid rich domain, followed by two EGFlike domains. The heavy chain consists of the serine protease catalytic domain. The gene for FVII is located on chromosome 13 at q34-qter, spans 12.8 kilobase pairs, and contains exons 1a and 1b (which encode the 5' untranslated region and most of the pre-pro leader sequence) and exons 2 to 8 (which encode the mature protein).
Factor VII (FVII) participates in the initial stages of blood coagulation. It is a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein that is synthesized in the liver, secreted into the blood and circulates as a single-chain zymogen composed of 406 amino acid residues with an approximate molecular weight of 50 kDa. The light chain consists of an aminoterminal γ-carboxyglutamic acid rich domain, followed by two EGFlike domains. The heavy chain consists of the serine protease catalytic domain. The gene for FVII is located on chromosome 13 at q34-qter, spans 12.8 kilobase pairs, and contains exons 1a and 1b (which encode the 5' untranslated region and most of the pre-pro leader sequence) and exons 2 to 8 (which encode the mature protein).FVII and FVIIa form a one-to-one stoichiometric complex with tissue factor TF on endothelium cells recruited by vessel damage. Once complexed to TF, FVII zymogen is converted to its active form by various coagulation proteases such as FXa. The TF-FVIIa complex readily activates zymogen FX and FIX to active enzymes and promotes f ibrin-formation.
Hereditary FVII def iciency is a rare autosomal recessive bleeding disorder that has an estimated prevalence of one per 500,000 in the general population.
FVII knockout mice die at birth, or shortly after, from major abdominal and intracranial hemorrhaging. In humans, the clinical phenotype exhibited by patients with FVII def iciency correlates with poor diagnostic laboratory tests.
Dif f erences between the clinical and laboratory phenotypes may be due to the complexity of biochemical interactions that occur with the initiation of hemostasis or because of a lack of sensitivity and accuracy in the assays used to measure very low levels of FVII:C.
We have reported various problematic issues with currently available commercial reagents and/or reference standard plasma.
However, no data regarding the inter-laboratory variability of FVII:C determinations in samples with low to very low FVII:C have so far been reported. It is very important to compare the results of dif f erent determinations of FVII def iciency for accurate diagnosis and treatment. We distributed three def icient plasma samples prepared via immunoaf f inity chromatography among 58 laboratories in Japan. These samples were measured using the routine protocol in place at each laboratory and a calibration reference plasma and recombinant thromboplastin were supplied as common reagents. We conclude that the results of the FVII:C assays, especially for cases with very low to low FVII:C concentrations, are greatly inf luenced by the number of plasma dilutions used in constructing a standard activity curve in additional to the type of thromboplastin and calibration plasma utilized to perform the tests. These results should prove useful in the development of more sensitive and accurate systems to measure FVII:C for the diagnosis and therapy of FVII def iciency.
主な業績論文等
- Properties of a recombinant bovine tissue factor expressed by Silkworm pupae and its performance as an Owren-type prothrombin time reagent for warfarin monitoring. Thrombosis Research. 130:520-527. 2012 Okuda M, Taniguchi T, Takamiya O.
- Factor VII def iciency due to compound heterozygosity for Lue-48Pro mutation and a novel Pro260Leu mutation. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis and Haemostasis 17:E205-210 2011 Kogiso N, Taki M, Takamiya O
- Japanese collaborative study to assess inter-laboratory variation in factor VII activity assays. Journal of Thrombosis Haemostasis 5: 1686-1692, 2007 Takamiya O,Ishikawa S, Ohnuma O, Suehisa H, Iijima K, Kayamori Y, Bando S, Higashi K
- Molecular mechanism of dysfunctional factor VII associated with the homozygous missense mutation 331Gly to Ser. Thrombosis Haemostasis 93: 414- 419, 2005. Takamiya O, Kimura S
- A patient homozygous for a Gly345Cys mutation in factor VII that results in severely impaired secretion of the molecule, but not complete def iciency. British Journal of Haematology 124:336-342, 2004. Takamiya O, Hino K






