フロンティアバイオサイエンス学科
 宇佐美 昭二(うさみ・しょうじ)
宇佐美 昭二(うさみ・しょうじ)
Shoji Usami
専門分野/植物分子生物学、植物生理学、植物病理学研究キーワード/藻類、水生植物、遺伝子組換え、細胞内情報伝達、教育教材
職位:教授
学位:理学博士(名古屋大学)
- 名古屋大学大学院理学研究科博士後期課程修了
- 通産省工業技術院微生物工業技術研究所研究員、名古屋大学理学部生物学科助手、広島大学大学院先端物質科学研究科准教授を経て本学へ
研究テーマ
(1)微細緑藻における細胞内情報伝達系の解析
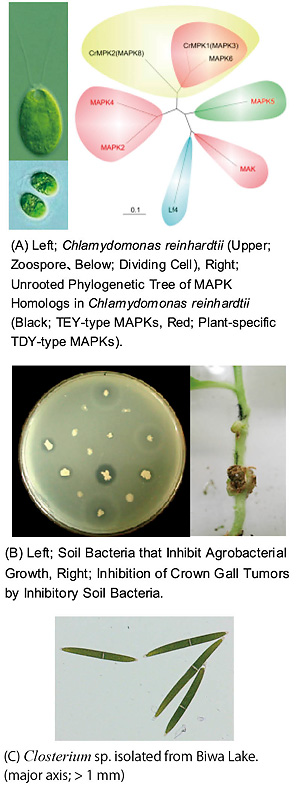
微細緑藻における細胞増殖・分化・代謝制御等に関わるMAPキナーゼ情報伝達系は未知な点が多い。単細胞性微細緑藻クラミドモナス(Chlamydomonas reinhardtii)には、MAPキナーゼ相同遺伝子が8種、高等植物と類似性を示すものは5種と極めて単純であり、高等植物のモデル系として最適である(図A)。5種のうち3種(CrMPK1, CrMPK2, MAPK6)は細胞増殖制御に関わることを明らかにした。一方、植物固有TDY型MAP キナーゼ MAPK2, MAPK4 には機能制御ドメインと予想される特徴的なアミノ酸配列が見出され、植物における機能解析に有用と期待される。
(2)植物根頭がんしゅ病抑制細菌の機能解析
植物根頭がんしゅ病菌 Agrobacterium tumefaciens は植物細胞へ遺伝子導入を行う細菌として有名である。一方、本来植物に腫瘍を誘発する植物病原菌であるとともに、種々の物質生産を行う有用菌でもある。本細菌の遺伝子改変による有用物質生産を目指すとともに、土壌内における他種土壌細菌群との相互作用を解析することにより、効果的な根頭がんしゅ病防除剤の開発等につながることが期待される(図B)。
(3)有用微細藻類や植物固有種の育種と利用
琵琶湖周辺には、ミカヅキモなどの微細藻類や植物固有種が多数生育している。それら微細藻類を分離・純化・育種を行うとともに(図C)、植物固有種の育成・活用化を目指している。
(4) 小中高校生向け実験教材の開発
近年の若者の理科離れに対する大学の地域貢献として、小中高校生向けの教材開発を行ってきた。学習指導要領に沿いながらより発展的に、小中高校教員自身でも指導可能な実験教材の開発を行っている。小学生向けにはプランクトン観察実験や植物吸水実験などを、中学生向けには細胞分裂観察実験などを、高校生向けには簡易DNA抽出法、手動PCR 実験などの開発を行ってきた。
| 研究の応用領域 | 産官学連携で求めるパートナー |
|---|---|
| 微細藻類・植物固有種の改良・育種、土壌細菌による有用物質・土壌改良剤の開発、小中高校・一般向け実験教材 | 実験教材開発関連企業、微細緑藻・植物の開発関連企業、農業資材開発関連企業、農業関連研究・試験場など |
Topics of research
1. MAPK transduction pathways in green algae
MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) transduction pathway is one of most famous intracellular signal transduction pathways conserved in eukaryotic cells. They are concerned in regulation of cellular events such as cell division, dif f erentiation and apoptosis. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a unicellular green alga, is a simplest plant cell. Genomic information suggested that there are only 8 MAPK homologs in Chlamydomonas, 3 homologs (CrMPK1, CrMPK2 and MAPK6) are TEY-type and 2 homologs (MAPK2 and MAPK4) are plant-specif ic TDY-type. The 2 TDY-type MAPK homologs have encoded unique amino acid domains that might be required for regulation of MAPK's functions. The analysis of those plant-specif ic TDY-type MAPK homologs in Chlamydomonas may suggest the plant-specif ic function in higher plants.
2. Agrobacterium tumefaciens and soil bacteria
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a causative soil bacterium that induces crown gall tumors by introduction of T-DNA into recipient plant cells. The agrobacteria also produce some industrially important organic materials such as cellulose and curdlan. We have modif ied the agrobacteria genetically to over-produce or to recycle the cellulose and curdlan. Also, we have analyzed soil bacteria that suppress the formation of crown gall tumors by agrobacteria. There may be novel mechanisms to inhibit the formation of crown gall tumors.
3. Isolation and breeding of endemic microalgae and plant species around Biwa lake
There are many endemic microalgae and plant species around Biwa lake. They may be unique resources of industrially important materials such as medicine and oil. We are now breeding of the endemic microalgae species such as Closterium spp. that shows very long needle shape.
4. Development of scientific experiments for elementary- to high-school students
主な業績論文等
- Askora, A., Kawasaki, T., Usami, S., Fujie, M., and Yamada, T.: Host recognition and integration of f ilamentous phage φRSM in the phytopathogen, Ralstonia solanacearum. Virology, 384 69-76 (2009)
- Kawasaki, T., Shimizu, M., Satsuma, H., Fujiwara, A., Fujie, M., Usami, S., and Yamada, T.: Genomic characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum phage φRSB1, a T7-like wide-host-range phage. J. Bacteriol., 191 422-427 (2009)
- Alemzadeh, A., Fujie, M., Usami, S., Yoshizaki, T., Oyama, K., Kawabata, T., and Yamada, T.: ZMVHA-B1, the gene for subunit B of vacuolar H+-ATPase from the eelgrass Zostera marina L. is able to replace vma2 in a yeast null mutant. J. Biosci. Bioeng., 102 390-395 (2006)






