客員教授
 木曽 良明(きそ・よしあき)
木曽 良明(きそ・よしあき)
Yoshiaki Kiso
専門分野/生物有機化学、ペプチド科学、創薬科学
職位:客員教授
学位:薬学博士(京都大学)
- 京都大学大学院薬学研究科博士課程単位修得
- 京都大学薬学部助手、ピッツバーグ大学リサーチアソシエート、徳島大学薬学部助教授、京都薬科大学教授・創薬科学フロンティア研究センター長・薬学研究科長・瀋陽薬科大学客員教授を歴任。
研究テーマ
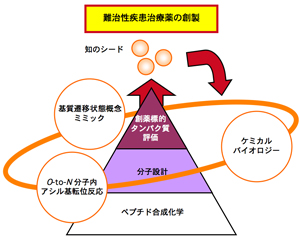
Fig. 1
ペプチド化学に基づく統合創薬科学の概念
ペプチド合成化学における保護基や縮合剤、そして分子内アシル基転位反応の研究などを基礎研究として行い、それらを利用して生物分子として重要なアミノ酸、ペプチド、タンパク質を重点標的として研究を進める。これを足場に、難治性疾患、特に感染症、アルツハイマー病、がん等の病原性に重要な役割を果たす生体タンパク分子の分子認識解析を基にしたリガンドや阻害剤のデザイン合成研究へと展開する。さらに、ケミカルバイオロジーの手法より分子設計にフィードバックを行い、より優れた治療薬の創製を目指す。筆者らが提唱する統合創薬科学の概念をFig. 1に示す。
(1)O-アシルイソペプチド法とクリックペプチド
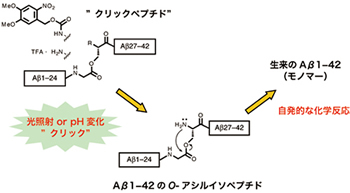
Fig. 2
O-アシルイソペプチドからのAβの生成(クリックペプチド)
新規ペプチド合成法「O-アシルイソペプチド法」を開発し、アルツハイマー病(AD)研究用ツールへと応用した。すなわち、アミロイドβペプチド(Aβ)のO-アシルイソペプチドを「クリックペプチド」と名付け、AD発症のメカニズムの核心に迫るツールを開発した。(Fig. 2)
(2)分子認識に基づくプロテアーゼ阻害剤
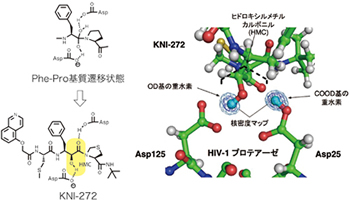
Fig. 3
KNI-272と中性子結晶構造解析によるHMCの水素結合相互作用
基質遷移状態ミミックとして独自のヒドロキシルメチルカルボニル(HMC)を提案し、基質アミノ酸配列にHMCを組込んだペプチドミメティック阻害剤をデザインした。中でも、トリペプチド型阻害剤のKNI-272は世界で初めての中性子結晶構造解析がなされ、HMCとHIVプロテアーゼ活性中心の2つのAsp残基との水素結合の様子が明らかになり、HMCが理想的な遷移状態アナログであることが実証された(Fig. 3)。
基質アミノ酸配列にHMCを組込んだ阻害剤設計の方法論は、他の疾患関連アスパラギン酸プロテアーゼの阻害剤にも適用できることから、マラリア治療薬を目指したプラスメプシン阻害剤(Fig. 4)、アルツハイマー病治療薬を目指したBACE1阻害剤(Fig. 5)の創薬研究へと展開させた。
中でもより強力でかつ四つのプラスメプシン全てに阻害活性を示すKNI-10006は「Science」でハイライトされ、著者らの方法論が紹介された。
また、KMI-429は低分子BACE1阻害剤として世界で初めてin vivoでの有効性が確認された。さらに、医薬品として実用化に向けた低分子化や血液脳関門透過性のある化合物へと構造変換を進めている。
| 研究の応用領域 | 産官学連携で求めるパートナー |
|---|---|
| 医薬品、診断薬、合成試薬の研究開発 | 医薬品、診断薬、合成試薬開発の関連企業、大学、国、地方自治体の研究機関 |
Topics of research
Basic research on protecting groups and coupling reagents in synthetic peptide chemistry and intramolecular acyl migration reaction are being carried out. The methodologies obtained are applied to biomolecular research on important amino acids, peptides and proteins as targets. The research results expand the design and synthesis of ligands and inhibitors based on molecular recognition analysis of biomolecules that play important roles in the pathogenesis of dif f icult diseases such as infectious diseases, Alzheimer’s disease and cancer. Furthermore, using chemical biology methodology, feedback on molecular design is carried out to achieve more excellent therapeutic drug development.

Fig. 4
Cover photo of Biochemistry 2012 cited from Biochemistry, 50, 8862 (2011).
Fig. 5
Cover photo of ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012 cited from ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 3, 193 (2012).
- O-Acyl Isopeptide method and Click Peptide
Newly developed peptide synthetic method “O-acyl isopeptide method” is being applied as a research tool for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The O-acyl isopeptide was named as “click peptide” and is developed as a tool that strikes the core mechanism of the onset of AD. - Protease inhibitors based on molecular recognition
The introduction of a unique hydroxymethylcarbonyl (HMC) group as a substrate transition state mimic led to the design of peptidomimetic inhibitors containing HMC. Among the inhibitors, a tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 was examined by neutron crystal structure analysis. The results showed the detailed hydrogen bonding interactions between HMC and the HIV protease’s active site’s Asp residues, demonstrating that HMC is the ideal transition state mimic.
The methodology of inhibitor design incorporating HMC into the substrate amino acid sequence is applicable to the design of other aspartic protease inhibitors related to other diseases. Therefore, the method is being developed to drug discovery research for plasmepsin inhibitors targeting malaria and BACE1 inhibitors for AD.
Among the inhibitors designed, an inhibitor KNI-10006 that shows potent inhibitory activity against all four plasmepsins was highlighted in Science.
KMI-429 was shown to be active in vivo for the f irst time among the low molecular BACE1 inhibitors ever reported. Furthermore, structural modif ications for size reduction and enhanced blood brain barrier permeability are being carried out to develop practical drugs.
主な業績論文等
- Adachi M, Ohhara T, Kurihara K, Tamada T, Honjo E, Okazaki N, Arai S, Shoyama Y, Kimura K, Matsumura H, Sugiyama S, Adachi H, Takano K, Mori Y, Hidaka K, Kimura T, Hayashi Y, Kiso Y, Kuroki R: Structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with potent inhibitor KNI-272 determined by high resolution X-ray and neutron crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 4641-4646 (2009).「生命を支える美しい分子たち」(化学と工業, 65, 117, 2012)で紹介される。
- Taniguchi A, Sohma Y, Hirayama Y, Mukai H, Kimura K, Hayashi Y, Matsuzaki K, Kiso Y: "Click peptide": pH-triggered in situ production and aggregation of monomer Aβ1-42. ChemBioChem, 10, 710-715 (2009) spotlighted in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 2444 (2009).
- Kiso Y, Taniguchi A, Sohma Y: Click peptides: design and applications. Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology, (ed. Tadhg P. Begley), Vol. 1, 379-383 (2009).
- Nezami A, Kimura T, Hidaka K, Kiso A, Liu J, Kiso Y, Goldberg D E, Freire E: High affinity inhibition of a family of Plasmodium falciparum proteases by a designed adaptive inhibitor. Biochemistry, 42, 8459-8464 (2003) highlighted in Science, 301, 143 (2003).
- Hofmann K, Finn F M, Kiso Y: Avidin-biotin affinity columns. General methods for attaching biotin to peptides and proteins. J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 100, 3585-3590 (1978).






