長谷川 慎
(はせがわ・まこと)
Makoto Hasegawa
略歴
- 大阪大学大学院理学研究科博士後期課程修了
- 東京工業大学フロンティア創造共同研究センター研究員を経て本学へ
蛋白質機能解析学研究室

卒業研究テーマ例
- タンパク質分解酵素複合体への阻害薬剤の持つ抗がん作用の研究
- 高度に微細加工された金属薄膜を利用した細胞分離技術の開発
- 環境中の微生物の分析技術に関する研究
「分子標的抗がん剤」の開発
「一分子蛍光分析法」を応用した感染症診断法の機器開発

微量物質の簡単検出を実現する「金属メッシュデバイス」センサーの開発
「試験管内人工進化法」による機能性ペプチドの創生
- 研究の応用領域
- 医薬品・診断薬の開発、バイオ分析機器の開発
- 産官学連携で求めるパートナー
- 医薬品・診断薬開発、材料やデバイス開発、微細加工の関連企業、バイオ機器メーカー、大学、国・地方自治体の研究機関
1
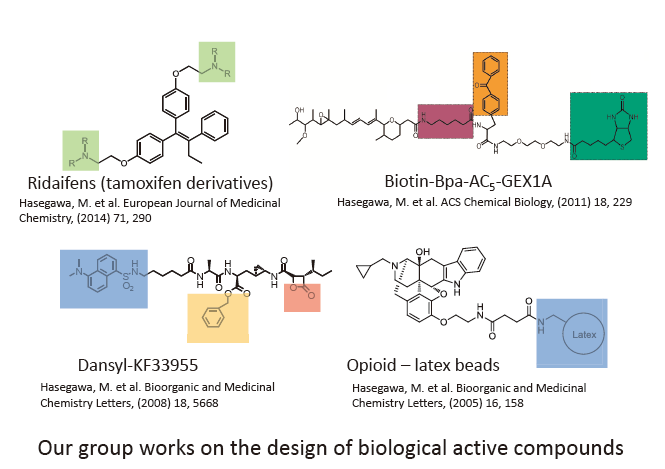
Proteosomal degradation of ubiquitinated proteins plays a pivotal role in the regulation of critical cell functions. Aberrant degradation of key regulatory proteins by the proteasome perturbs these functions, causing uncontrolled cell proliferation and decreased cell death, which are hallmarks of tumorigenesis. Indeed, several proteasome inhibitors have been proposed as anticancer drugs. However, many of these inhibitors have drawbacks, including side effects and short life-time. Thus, the development of new types of proteasome inhibitors is required to broaden the spectrum of inhibitors with fewer side-effects. In an attempt to search for new proteasome inhibitors, we have found that a novel tamoxifen (TAM) derivative, ridaifen-F (RID-F), inhibits the human 20S proteasome. Furthermore, we have prepared several conjugates that possess various peptides connected to RID-F. Conjugates with peptides consisting of seven amino acid residues significantly inhibited the 26S proteasome. Particularly, RID-F conjugated to an octaarginine peptide (a so-called cell-penetrating peptide) inhibited intracellular proteasome activities and induced cell death in a drug-resistant myeloma cell line. (See References No. 1 and 5)
2
We have designed and developed a compact immunosensor based on the principle of fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy. It enables us to detect fluorescence signals from assemblages of virus and fluorescence-labeled antibody. This prototype instrument detected rotavirus in stool suspensions using the fluorescence-labeled antibody without the need for a prior isolation step, providing a result within minutes. These features may be useful for point-of-care testing, as well as the prevention and eradication of viral infections. (See Reference No. 2)
3
A metal mesh device (MMD) is a thin nickel mesh with periodic microstructures consisting of square apertures. The MMD operating as a band-path filter in the range of 100 THz electromagnetic waves is suitable for optically sensing mesh-captured particles, and simultaneously functions as a sieve for separating particles according to their size. We are developing techniques using this MMD to selectively capture and detect particular cells from a mixture containing other types of cells. The MMD is useful for recovery of cultured cells from cultures without cellular damage, which may facilitate large-scale culture in cell biotechnology, because centrifugation, a laborious process for harvesting cells, becomes dispensable. (See Reference No. 3)
Tanaka M, Zhu Y, Shionyu M, Ota N, Shibata N, Watanabe C, Mizusawa A, Sasaki R, Mizukami T, Shiina I, Hasegawa M (2018) Ridaifen-F conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides inhibits intracellular proteasome activities and induces drug-resistant cell death. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 146, 636–650.
Hasegawa M, Wandera EA, Inoue Y, Kimura N, Sasaki R, Mizukami T, Shah MM, Shirai N, Takei O, Shindo H, Ichinose Y (2017) Detection of rotavirus in clinical specimens using an immunosensor prototype based on the photon burst counting technique. Biomedical Optics Express 8, 3383-3394.
Hasegawa M, Yamamoto K, Shirai-Kitanishi E, Mori K, Inoue Y, Inagaki Y, Sasaki R, Mizukami T, Shirai M, Miura Y, Ogawa Y, Banju M, Kamba S, Kondo T (2016) Surface coating of a metal mesh device sensor with gold to improve the separation and sensing of mammalian cell. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16, 5129-5135.
Hayakawa Y, Matsuno M, Tanaka M, Wada A, Kitamura K, Takei O, Sasaki R, Mizukami T, Hasegawa M (2015) Complementary DNA display selection of high-affi nity peptides binding the vacuolating toxin (VacA) of Helicobacter pylori. Journal of Peptide Science 21, 710-716.
Hasegawa M, Yasuda Y, Tanaka M, Nakata K, Umeda E, Wang Y, Watanabe C, Uetake S, Kunoh T, Shionyu M, Sasaki R, Shiina I, Mizukami T (2014) A novel tamoxifen derivative, ridaifen-F, is a non-peptidic and small-molecule proteasome inhibitor. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 71, 290-305.






